-40%
Big-head Ant and Termite in 75x75x10 mm Clear Square Slide Education Specimen
$ 6.85
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
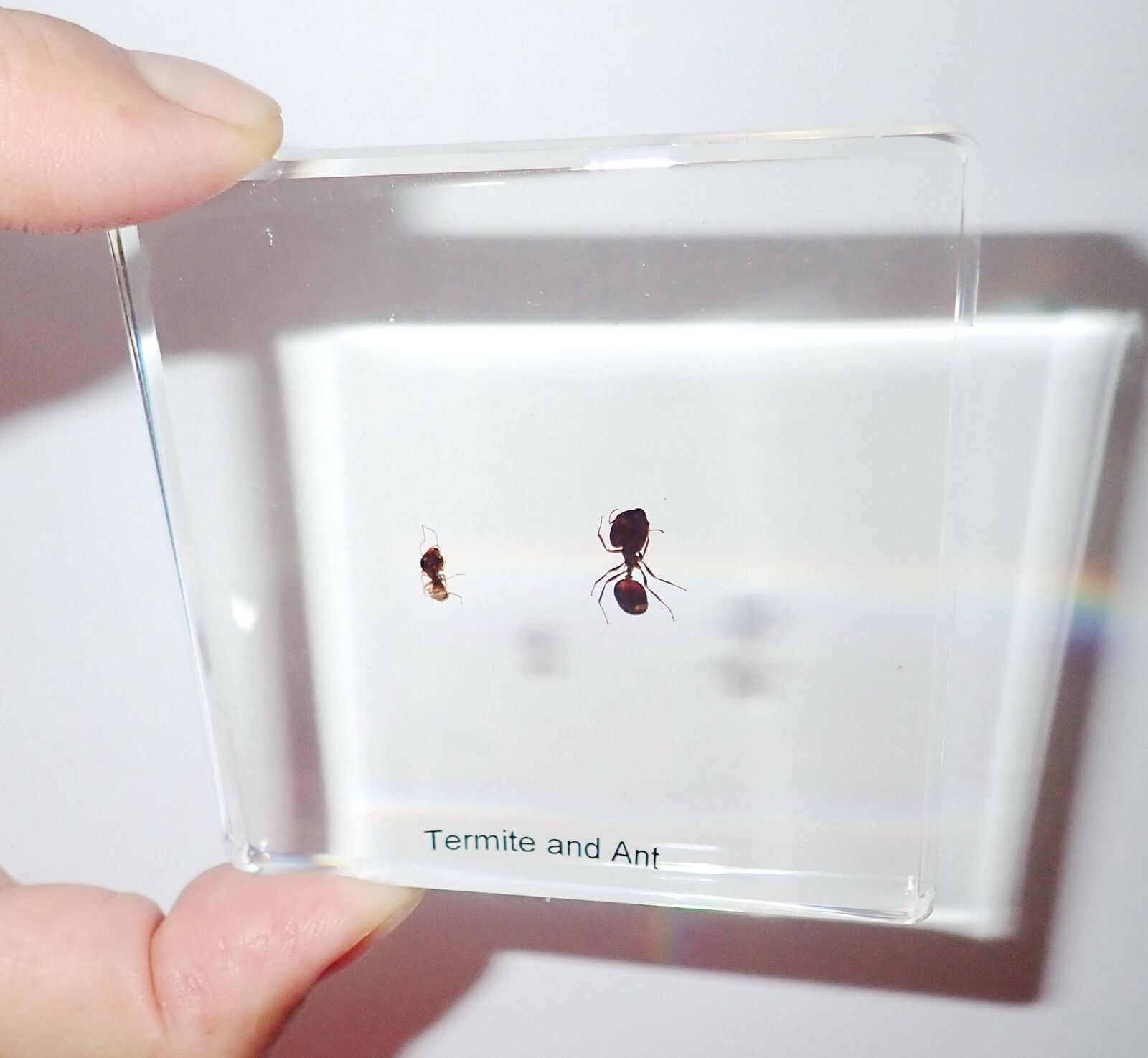
Real Big-head Ant - Pheidologeton diversus and The Termite - Macrotermes bellicosus specimen encased in clear lucite material. The specimens are crystal clear, indestructible and transparent. Safe, authentic and completely unbreakable product put real specimens right at your fingertips!Anyone can safely explore the specimens from every angle.
It is clear enough for microscope observation.
Length of the ant and termite body is 1.2 cm, 0.6 cm (0.5, 0.3 inch).
Size of the lucite block is 75x75x9 mm (3x3x0.4 inch).
Each one comes with a cardboard box for easy storage.
Weight of the lucite block is 60 g and 90 g with packing box.
Selltotheworld
From all around the world
Big-head Ant and Termite in 75x75x10 mm Clear Square Slide Education Specimen
Real
Big-head Ant -
Pheidologeton diversus
and
The Termite -
Macrotermes bellicosus
specimen encased in clear lucite material. The specimens are crystal clear, indestructible and transparent. Safe, authentic and completely unbreakable product put real specimens right at your fingertips!
Anyone can safely explore the specimens from every angle.
It is clear enough for microscope observation.
Length of the ant and termite body is 1.2 cm, 0.6 cm (0.5, 0.3 inch).
Size of the lucite block is 75x75x9 mm (3x3x0.4 inch).
Each one comes with a cardboard box for easy storage.
Weight of the lucite block is 60 g and 90 g with packing box.
It is an ideal learning aid for students and kids and also a very good collectible item for every body.
This is a handmade real animal specimen craft. Each one will be a bit different (specimen size, color and posture) even in the same production batch.
The pictures in the listing are just for reference as we are selling multiple pieces with same pictures.
***
Big-head A
nt
-
Pheidologeton diversus
Family:Formicidae Subfamily:Myrmicinae Tribe:Pheidolini Genus:
Pheidole
Distribution: Tropical and sub-tropical Asia
(China, Taiwan, Japan)
Description
: Total length between 1.3 and 2.5 mm in minor workers. Body color yellowish brown to reddish brown in minor workers: reddish brown to blackish brown in majors. In minor workers: head rectangular with weakly convex posterior margin in full face view; mandibles each with 5 teeth; antennal scapes short, not exceeding posterior margin of head; each of the apical two funicular segments long, their combined length longer than the rest of funiculus; promesonotum relatively strongly convex in profile; metanotal groove deeply incised; dorsum of propodeum convex; propodeal spines long, with acute apices. In major workers: head proportionately large, almost square, with convex posterior margin in frontal view; anterior margin of clypeus straight, with a shallow median notch; mandibles large, triangular, with an acute apical tooth; masticatory margins without distinct teeth; eyes relatively small; ocelli present; antennal scapes 0.5 times as long as head; subpetiolar process present.
The Termite -
Macrotermes bellicosus
Order:
Macrotermitinae
Family: Termitidae Subfamily:
Macrotermitinae
Genus:
Macrotermes
Macrotermes bellicosus
is one of nearly 2000 species of termites, and the genus Macrotermes is widely distributed throughout Africa and South-East Asia. The species M. bellicosus is one of the largest termites, with a complex, highly evolved colonial organization. All termites live in colonies, those of M. bellicosus reaching a size of hundreds of thousands over many years. Although termites are sometimes called "white ants", they are not ants, nor are they closely related to them.
The nest.
Some termites build nests in wood, some in trees and posts, and some below the ground but M. bellicosus, though it begins its nest below ground, forms large mounds or towers of soil. The nest is constructed of sand and clay. The workers burrow into the subsoil bringing back a sand grain and a "mouthful" of clay which becomes moistened with saliva. The sand particle is stuck in position in the nest and cemented with the mortar of clay and saliva. Building activities are most intense at the beginning of the wet season.
If clay is abundant in the subsoil and rainfall is low, the nest is a tapering column up to 9 metres high, but if clay is in short supply and the rainfall is high, the building material cannot withstand the eroding action of rain, and a dome-shaped nest, about 2 metres high, results. The mound does not appear until the colony is several years old but thereafter it grows rapidly, reaching perhaps one-third of its final height in the first year.
The main part of the colony, the "hive", is in the mound just above ground level and inside the mound is a maze of passages, some of which lead away under the soil to reach supplies of wood and vegetation up to 100 metres away. One or more vertical shafts run to the summit of the nest.
Inside the nest, the temperature is fairly constant at about 30oC and often lower than outside, and the humidity also remains steady at about 90 per cent. This high humidity keeps the nest material permanently plastic and the internal architecture of the nest is constantly being altered. The interior of the nest provides an almost unvarying environment, making the termites independent of changes in climate outside. Even if termites have to pass over the ground in search of food, they construct covered runways which protect them from drying out and from certain predators.
Food.
On the whole, termites live on the cellulose of woody vegetation, many species burrowing into dead wood of trees and in buildings. There is no cellulose-digesting enzyme in the termite's body, and so indirect methods of digestion are important. Some species have single-celled organisms (protozoa) in their intestines and it is these protozoa which digest the cellulose, while the protozoa themselves are a source of food for the termite. Macrotermes bellicosus has no intestinal protozoa but constructs fungus combs in the nest.
The fungus combs consist of spongy masses of wood-pulp derived from the faeces, covered with a mycelium of fungal hyphae and sporangia. It seems very likely that the fungus digests the wood to a stage that can be utilized by the termites.
Life cycle.
Termites undergo incomplete metamorphosis, but most of the individuals in a colony remain as nymphs and function as workers or soldiers. The workers collect food, chew wood-pulp, enlarge and repair the nest, make tunnels, and look after the queen, the eggs and young nymphs. The soldiers keep ants out of the nest by snapping their large jaws or blocking the tunnels with their heads.
Just before the rainy season, some of the nymphs continue their metamorphosis, developing reproductive organs and wings. Early in the rainy season, these mature termites (reproductives) swarm; that is, they emerge in their hundreds from the nest at night and fly off into the surrounding countryside. The males and females mate and start a new colony. As soon as there are enough worker nymphs to maintain the nest, the queen settles down to uninterrupted egg-laying. Her abdomen swells enormously and the workers wall her up in the nest, bring her food and take away the eggs as fast as she lays them.
Economic importance.
Although termites normally eat dead vegetation, their tunnels may weaken plant stems, causing them to collapse or giving access to fungus and other diseases. Where bark is gnawed from trees, the phloem may be interrupted, causing the death of the tree. The mud runways with which some species cover the plants to reach dead wood may cause the plant, e.g. tea, to wither and collapse. Cocoa trees, sugar cane, young coconut trees, cotton and wheat plants are among crops that may be affected by termites. Macrotermes is not of very great importance in this respect but its nest-mounds get in the way of agricultural machinery and have to be blown up with explosives or levelled with bulldozers, thus increasing the cost of mechanized farming, road construction and building-site clearance. Perhaps the most familiar termite damage is to the wooden fabric of buildings and furniture. Various earth-dwelling species, though not M. bellicosus, tunnel underground from their nests and enter the building through its foundations or any wooden part in contact with the ground. To obtain the wood for their food they make extensive tunnels through the structures, weakening them and eventually causing their collapse. Since the insects make no openings to the outside, or do so only at an advanced stage of the invasion, the owner is frequently unaware of their presence until it is too late.
Prevention of termite damage.
Buildings should be constructed on solid concrete or be raised on masonry piers. In either case, termites may still gain access by building their covered runways over the masonry to reach the wood. A projecting ledge round the concrete base or pier will prevent even this method of access. Great care must be taken to see that no unprotected wooden part of the building, (e.g. steps) is in contact with the ground.
The earth round the building can be impregnated with insecticides which may prevent the termites tunnelling through to the structures for several years. None of these precautions is proof against the species of termites which fly to buildings and establish nests in the woodwork. The only measure against this type of invasion is to use wood which is naturally resistant to termite attack or that has been soaked in chemicals which repel the insects.
Predators.
Vast numbers of winged termites are eaten at the time of swarming. In the air they are snapped up by birds such as hawks and swallows, and on the ground by lizards, toads and spiders. In the nest, the termites are subject to attacks by "ant-eating" mammals such as the ant-bear or aardvark which burrows into the mound and licks out the termites with a long, thin tongue. The covered, over-ground runways are broken open to reach the termites within by birds of various kinds.
Humans and ants are also the enemies of termites. Ants carry off the workers that are working outside the nest and may invade and destroy a colony; humans capture and eat the swarming
reproductives or dig out the queen as a special delicacy.
Item Specifics
Handmade :
Yes
Modified Item :
No
Country/Region of Manufacture :
China
Material :
Resin
Type :
Collector Plate
Material :
Resin
Type :
Collector Plate
Payment
By Paypal
Shipping
Free shipping cost.
We send the goods to USA, Canada, UK, Australia, New Zealand, EU countries and some other European and Asian countries by E-express, a kind of fast postal service by Hong Kong Post. It usually takes about 6 to 10 working days for delivery.
We send the goods to other countries by registered airmail and will take about 8 to 14 working days for delivery.
Returns
Returns: We accept returns with any reason in 30 days.
Contact Us
We will answer buyer messages within 24 hours during working days.
Selltotheworld
From all around the world
DESCRIPTION
PAYMENT
SHIPPING
RETURN POLICY
CONTACT US
Big-head Ant and Termite in 75x75x10 mm Clear Square Slide Education Specimen
Real
Big-head Ant -
Pheidologeton diversus
and
The Termite -
Macrotermes bellicosus
specimen encased in clear lucite material. The specimens are crystal clear, indestructible and transparent. Safe, authentic and completely unbreakable product put real specimens right at your fingertips!
Anyone can safely explore the specimens from every angle.
It is clear enough for microscope observation.
Length of the ant and termite body is 1.2 cm, 0.6 cm (0.5, 0.3 inch).
Size of the lucite block is 75x75x9 mm (3x3x0.4 inch).
Each one comes with a cardboard box for easy storage.
Weight of the lucite block is 60 g and 90 g with packing box.
It is an ideal learning aid for students and kids and also a very good collectible item for every body.
This is a handmade real animal specimen craft. Each one will be a bit different (specimen size, color and posture) even in the same production batch.
The pictures in the listing are just for reference as we are selling multiple pieces with same pictures.
***
Big-head A
nt
-
Pheidologeton diversus
Family:Formicidae Subfamily:Myrmicinae Tribe:Pheidolini Genus:
Pheidole
Distribution: Tropical and sub-tropical Asia
(China, Taiwan, Japan)
Description
: Total length between 1.3 and 2.5 mm in minor workers. Body color yellowish brown to reddish brown in minor workers: reddish brown to blackish brown in majors. In minor workers: head rectangular with weakly convex posterior margin in full face view; mandibles each with 5 teeth; antennal scapes short, not exceeding posterior margin of head; each of the apical two funicular segments long, their combined length longer than the rest of funiculus; promesonotum relatively strongly convex in profile; metanotal groove deeply incised; dorsum of propodeum convex; propodeal spines long, with acute apices. In major workers: head proportionately large, almost square, with convex posterior margin in frontal view; anterior margin of clypeus straight, with a shallow median notch; mandibles large, triangular, with an acute apical tooth; masticatory margins without distinct teeth; eyes relatively small; ocelli present; antennal scapes 0.5 times as long as head; subpetiolar process present.
The Termite -
Macrotermes bellicosus
Order:
Macrotermitinae
Family: Termitidae Subfamily:
Macrotermitinae
Genus:
Macrotermes
Macrotermes bellicosus
is one of nearly 2000 species of termites, and the genus Macrotermes is widely distributed throughout Africa and South-East Asia. The species M. bellicosus is one of the largest termites, with a complex, highly evolved colonial organization. All termites live in colonies, those of M. bellicosus reaching a size of hundreds of thousands over many years. Although termites are sometimes called "white ants", they are not ants, nor are they closely related to them.
The nest.
Some termites build nests in wood, some in trees and posts, and some below the ground but M. bellicosus, though it begins its nest below ground, forms large mounds or towers of soil. The nest is constructed of sand and clay. The workers burrow into the subsoil bringing back a sand grain and a "mouthful" of clay which becomes moistened with saliva. The sand particle is stuck in position in the nest and cemented with the mortar of clay and saliva. Building activities are most intense at the beginning of the wet season.
If clay is abundant in the subsoil and rainfall is low, the nest is a tapering column up to 9 metres high, but if clay is in short supply and the rainfall is high, the building material cannot withstand the eroding action of rain, and a dome-shaped nest, about 2 metres high, results. The mound does not appear until the colony is several years old but thereafter it grows rapidly, reaching perhaps one-third of its final height in the first year.
The main part of the colony, the "hive", is in the mound just above ground level and inside the mound is a maze of passages, some of which lead away under the soil to reach supplies of wood and vegetation up to 100 metres away. One or more vertical shafts run to the summit of the nest.
Inside the nest, the temperature is fairly constant at about 30oC and often lower than outside, and the humidity also remains steady at about 90 per cent. This high humidity keeps the nest material permanently plastic and the internal architecture of the nest is constantly being altered. The interior of the nest provides an almost unvarying environment, making the termites independent of changes in climate outside. Even if termites have to pass over the ground in search of food, they construct covered runways which protect them from drying out and from certain predators.
Food.
On the whole, termites live on the cellulose of woody vegetation, many species burrowing into dead wood of trees and in buildings. There is no cellulose-digesting enzyme in the termite's body, and so indirect methods of digestion are important. Some species have single-celled organisms (protozoa) in their intestines and it is these protozoa which digest the cellulose, while the protozoa themselves are a source of food for the termite. Macrotermes bellicosus has no intestinal protozoa but constructs fungus combs in the nest.
The fungus combs consist of spongy masses of wood-pulp derived from the faeces, covered with a mycelium of fungal hyphae and sporangia. It seems very likely that the fungus digests the wood to a stage that can be utilized by the termites.
Life cycle.
Termites undergo incomplete metamorphosis, but most of the individuals in a colony remain as nymphs and function as workers or soldiers. The workers collect food, chew wood-pulp, enlarge and repair the nest, make tunnels, and look after the queen, the eggs and young nymphs. The soldiers keep ants out of the nest by snapping their large jaws or blocking the tunnels with their heads.
Just before the rainy season, some of the nymphs continue their metamorphosis, developing reproductive organs and wings. Early in the rainy season, these mature termites (reproductives) swarm; that is, they emerge in their hundreds from the nest at night and fly off into the surrounding countryside. The males and females mate and start a new colony. As soon as there are enough worker nymphs to maintain the nest, the queen settles down to uninterrupted egg-laying. Her abdomen swells enormously and the workers wall her up in the nest, bring her food and take away the eggs as fast as she lays them.
Economic importance.
Although termites normally eat dead vegetation, their tunnels may weaken plant stems, causing them to collapse or giving access to fungus and other diseases. Where bark is gnawed from trees, the phloem may be interrupted, causing the death of the tree. The mud runways with which some species cover the plants to reach dead wood may cause the plant, e.g. tea, to wither and collapse. Cocoa trees, sugar cane, young coconut trees, cotton and wheat plants are among crops that may be affected by termites. Macrotermes is not of very great importance in this respect but its nest-mounds get in the way of agricultural machinery and have to be blown up with explosives or levelled with bulldozers, thus increasing the cost of mechanized farming, road construction and building-site clearance. Perhaps the most familiar termite damage is to the wooden fabric of buildings and furniture. Various earth-dwelling species, though not M. bellicosus, tunnel underground from their nests and enter the building through its foundations or any wooden part in contact with the ground. To obtain the wood for their food they make extensive tunnels through the structures, weakening them and eventually causing their collapse. Since the insects make no openings to the outside, or do so only at an advanced stage of the invasion, the owner is frequently unaware of their presence until it is too late.
Prevention of termite damage.
Buildings should be constructed on solid concrete or be raised on masonry piers. In either case, termites may still gain access by building their covered runways over the masonry to reach the wood. A projecting ledge round the concrete base or pier will prevent even this method of access. Great care must be taken to see that no unprotected wooden part of the building, (e.g. steps) is in contact with the ground.
The earth round the building can be impregnated with insecticides which may prevent the termites tunnelling through to the structures for several years. None of these precautions is proof against the species of termites which fly to buildings and establish nests in the woodwork. The only measure against this type of invasion is to use wood which is naturally resistant to termite attack or that has been soaked in chemicals which repel the insects.
Predators.
Vast numbers of winged termites are eaten at the time of swarming. In the air they are snapped up by birds such as hawks and swallows, and on the ground by lizards, toads and spiders. In the nest, the termites are subject to attacks by "ant-eating" mammals such as the ant-bear or aardvark which burrows into the mound and licks out the termites with a long, thin tongue. The covered, over-ground runways are broken open to reach the termites within by birds of various kinds.
Humans and ants are also the enemies of termites. Ants carry off the workers that are working outside the nest and may invade and destroy a colony; humans capture and eat the swarming
reproductives or dig out the queen as a special delicacy.
Item Specifics
Handmade :
Yes
Modified Item :
No
Country/Region of Manufacture :
China
Material :
Resin
Type :
Collector Plate
Material :
Resin
Type :
Collector Plate
Payment
By Paypal
Shipping
Free shipping cost.
We send the goods to USA, Canada, UK, Australia, New Zealand, EU countries and some other European and Asian countries by E-express, a kind of fast postal service by Hong Kong Post. It usually takes about 6 to 10 working days for delivery.
We send the goods to other countries by registered airmail and will take about 8 to 14 working days for delivery.
Returns
Returns: We accept returns with any reason in 30 days.
Contact Us
We will answer buyer messages within 24 hours during working days.
All right reserved.
Shop Category
Store Home
Fossils
◈ Insects
◈ Plants
◈ Trilobite
◈ Sea animals
Tektite
◈ Loose lots
◈ Single stone
◈ Silver wired pendant
◈ Tiktite hanger
Lapis Lazuli
▷ Polished stones
♢ Loose lots
♢ Single stones
▷ Rough stones
♢ Loose lots
♢ Single stone
◈ Craft items
Turquoise
◈ Natural turquoise
◈ Turquoise substitutes
Stone carving
Rough Stone & mineral
◈ Single piece
◈ Loose lots
Polished Stone & mineral
◈ Single piece
◈ Loose lots
Rough ruby & sapphire
◈ Ruby
◈ Sapphire
Star Ruby & Sapphire
◈ Star Ruby - Opaque
◈ Star Ruby - Transparent
◈ Blue Star Sapphire
◈ Star Sapphire - other colors
Animal specimen items
◈ Life cycle
◈ Collection set
◈ Key ring
◈ Bracelet or bangle
◈ Necklace or pendant
◈ Magnet
◈ Ring
◈ Hanger
◈ Cabochon
◈ Sphere, ball
◈ Laminated specimen
◈ Computer mouse
◈ Stapler
◈ Pen
◈ Bottle Opener
◈ Dome paperweight
◈ Earring
◈ Skeleton
◈ Fish
▷ Single specimens
♢ Spider
♢ Scorpion
♢ Beetle
♢ Marine animal
♢ Bug
♢ Bee, wasp, hornet
♢ Other insects
♢ Bat
♢ Other animal
▷ Butterfly
♢ Butterfly paperweight
♢ Laminated butterfly
Plant specimen
◈ Flower
◈ Leaf
◈ Life Cycle
◈ Collection Set
◈ Laminated items
◈ Seed or root
Stone, mineral, fossil box set
Jewelry crafts
Paper cuts
◈ Small set
◈ Large set
◈ Single piece
Other
Hot Item
Chinese Water Snake Skeleton in 110x45x18 mm Block Education Animal Specimen
USD 35.00
Spotted Lanternfly Cicada Life Cycle Simplified Set Real Specimen Learning Aid
USD 18.00
10 Mohs Scale Stone Set clear plastic box Learning Real Specimen Kit
USD 20.00
Black Indochinite Tektite Stone 10 pieces Plastic Box Set Natural Specimen Kit
USD 18.00
Insect Cabochon Golden Scorpion Oval 18x25 mm on black bottom 5 pieces Lot
USD 17.00
Picture
New List Item
Large Key Ring Red Neck Longhorn Beetle YK83 Glow
USD 12.99
Turquoise Stone Oval 11x9 mm Flat Cabochon 65 Carat 25 pieces 13 gram
USD 31.99
Turquoise Stone Oval 24x10 mm Flat Cabochon 66 Carat 10 pieces 13.2 gram
USD 22.99
Turquoise Stone Flat Free Form Cabochon 134.5 Carat 4 pieces 26.9 gram Lot B
USD 23.99
Turquoise Stone Oval 24x10 mm Flat Cabochon 66 Carat 10 pieces 13.2 gram
USD 22.99
Custom Item